5.5 KiB
| title | sidebar_label |
|---|---|
| Hold-Tap Behavior | Hold-Tap |
Summary
Hold-tap is the basis for other behaviors such as layer-tap and mod-tap.
Simply put, the hold-tap key will output the 'hold' behavior if it's held for a while, and output the 'tap' behavior when it's tapped quickly.
Hold-Tap
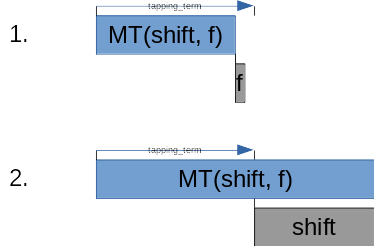
The graph below shows how the hold-tap decides between a 'tap' and a 'hold'.
By default, the hold-tap is configured to also select the 'hold' functionality if another key is tapped while it's active:
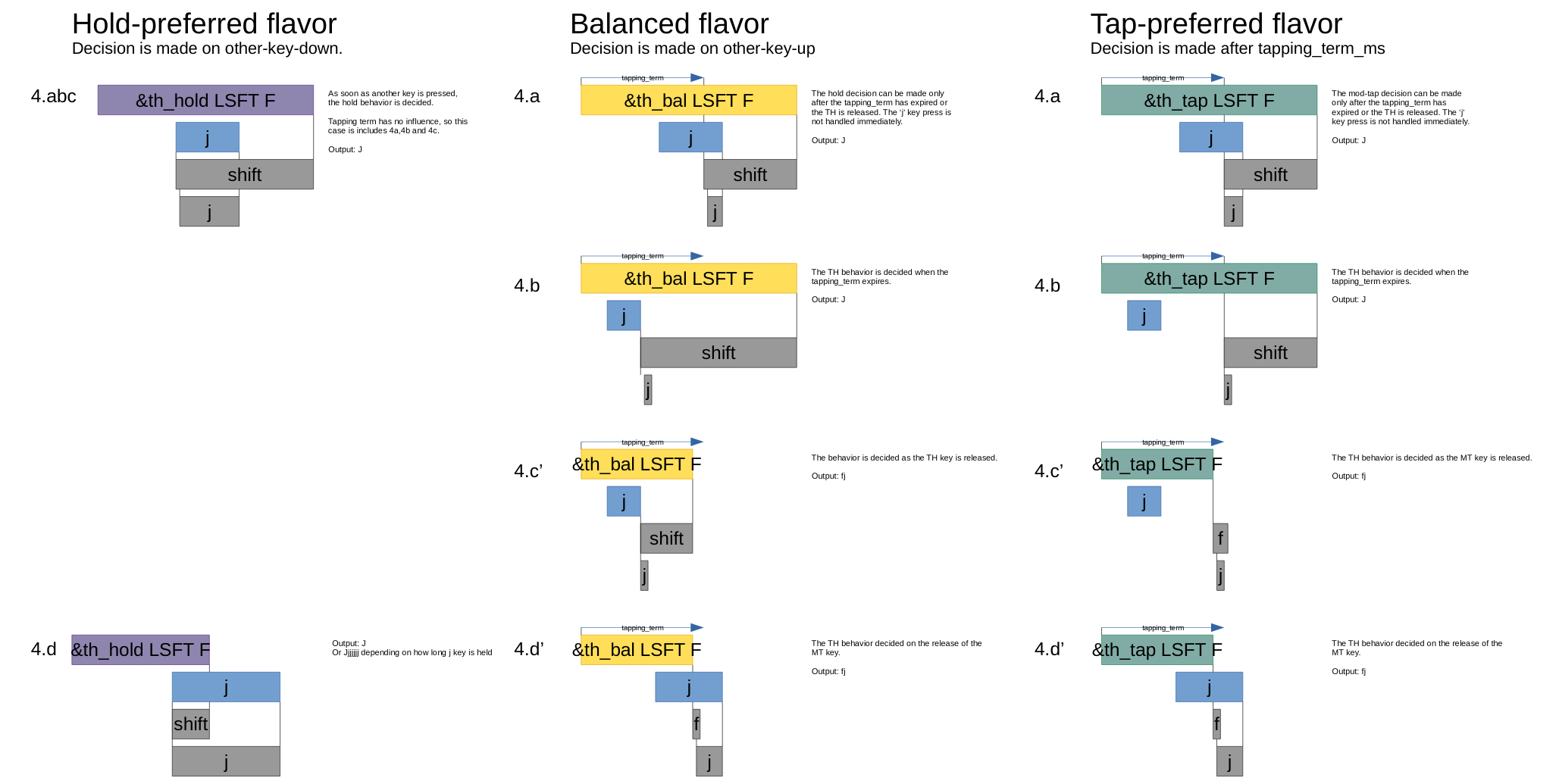
We call this the 'hold-preferred' flavor of hold-taps. While this flavor may work very well for a ctrl/escape key, it's not very well suited for home-row mods or layer-taps. That's why there are two more flavors to choose from: 'tap-preferred' and 'balanced'.
Flavors
- The 'hold-preferred' flavor triggers the hold behavior when the
tapping-term-mshas expired or another key is pressed. - The 'balanced' flavor will trigger the hold behavior when the
tapping-term-mshas expired or another key is pressed and released. - The 'tap-preferred' flavor triggers the hold behavior when the
tapping-term-mshas expired. It triggers the tap behavior when another key is pressed.
When the hold-tap key is released and the hold behavior has not been triggered, the tap behavior will trigger.
Basic usage
For basic usage, please see mod-tap and layer-tap pages.
Advanced Configuration
tapping-term-ms
Defines how long a key must be pressed to trigger Hold behavior.
quick_tap_ms
If you press a tapped hold-tap again within quick_tap_ms milliseconds, it will always trigger the tap behavior. This is useful for things like a backspace, where a quick tap+hold holds backspace pressed. Set this to a negative value to disable. The default is -1 (disabled).
In QMK, unlike ZMK, this functionality is enabled by default, and you turn it off using TAPPING_FORCE_HOLD.
retro-tap
If retro tap is enabled, the tap behavior is triggered when releasing the hold-tap key if no other key was pressed in the meantime.
For example, if you press &mt LEFT_SHIFT A and then release it without pressing another key, it will output a.
&mt {
retro-tap;
};
Home row mods
This example configures a hold-tap that works well for homerow mods:
#include <behaviors.dtsi>
#include <dt-bindings/zmk/keys.h>
/ {
behaviors {
hm: homerow_mods {
compatible = "zmk,behavior-hold-tap";
label = "HOMEROW_MODS";
#binding-cells = <2>;
tapping-term-ms = <150>;
quick_tap_ms = <0>;
flavor = "tap-preferred";
bindings = <&kp>, <&kp>;
};
};
keymap {
compatible = "zmk,keymap";
default_layer {
bindings = <
&hm LCTRL A &hm LGUI S &hm LALT D &hm LSHIFT F
>;
};
};
};
If this config does not work for you, try the flavor "balanced" with a medium tapping-term-ms such as 200ms.
Positional hold-tap and hold-enabler-keys
Including hold-enabler-keys in your hold-tap behavior definition turns on positional hold-tap. This causes the hold-tap behavior to only be allowed to produce a hold behavior if the next key pressed is one of the hold-enabler-keys. For example, with the following configuration:
#include <dt-bindings/zmk/keys.h>
#include <behaviors.dtsi>
/ {
behaviors {
pht: positional_hold_tap {
compatible = "zmk,behavior-hold-tap";
label = "POSITIONAL_HOLD_TAP";
#binding-cells = <2>;
flavor = "hold-preferred";
tapping-term-ms = <400>;
quick-tap-ms = <200>;
bindings = <&kp>, <&kp>;
hold-enabler-keys = <1>; // <---[[the W key]]
};
};
keymap {
compatible = "zmk,keymap";
label ="Default keymap";
default_layer {
bindings = <
&cht LEFT_SHIFT Q &kp W &kp E
>;
};
};
};
The sequence (cht_down, W_down, W_up, E_down, E_up, cht_up) produces WE, because the positional hold-tap IS permitted to produce a hold behavior, because the next key pressed (the W key in position 1) IS one of the hold-enabler-keys.
Meanwhile, the sequence (cht_down, E_down, E_up, W_down, W_up cht_up) produces qew, because the positional hold-tap is NOT permitted to produce a hold behavior, because the next key pressed (the E key in position 2) is NOT one of the hold-enabler-keys.
Positional hold-taps can be useful with home-row modifiers for example. By setting hold-enabler-keys to include only the keys controlled by the opposite hand, positional hold-taps can prevent one-handed "rolls" from accidentally triggering hold behaviors.
Note that while for regular hold-tap behaviors a shorter tapping-term encourages hold decisions, the opposite is true for positional hold-tap behaviors. For positional hold-taps, a shorter tapping-term actually encourages tap decisions. This is because when the tapping-term expires, this triggers the behavior to decide as either a tap or a hold. But if the user has not yet had time to press one of the hold-enabler-keys, then the behavior will decide as a tap. Shortening the tapping-term thus gives the user less time to press one of the hold-enabler-keys to produce a hold behavior.
Comparison to QMK
The hold-preferred flavor works similar to the HOLD_ON_OTHER_KEY_PRESS setting in QMK. The 'balanced' flavor is similar to the PERMISSIVE_HOLD setting, and the tap-preferred flavor is similar to IGNORE_MOD_TAP_INTERRUPT.